C-Band Satellite Dishes have long been a cornerstone of satellite communications, providing reliable solutions for everything from television broadcasting to internet connectivity. Whether you're an internet service provider, broadcaster, or satellite network operator, understanding the capabilities of C-Band technology is essential. In this article, we’ll explore what C-Band Satellite Dishes are, their primary uses, the benefits they offer over other frequency bands, and how to properly set them up and maintain them.
Table of contents:
What is a C Band Satellite Dish?
Understanding the C-Band Frequency Range
The C-Band refers to a specific range of frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically falling between 4.0 and 8.0 GHz. However, for satellite communication, the most relevant portion is from 3.7 to 4.2 GHz for receiving signals and 5.925 to 6.425 GHz for transmitting. This frequency range is optimal for satellite communications because it balances signal strength and interference resistance, making it an ideal choice for various applications, especially where reliability is key.
Characteristics of C-Band Satellite Dishes
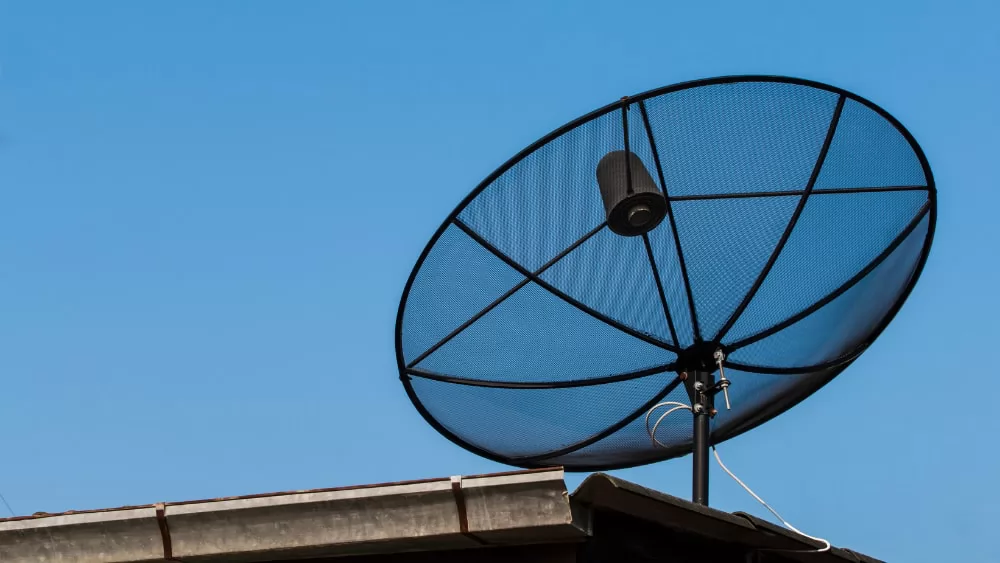
C-Band Satellite Dishes are large, parabolic antennas that are specifically designed to transmit and receive signals within this frequency range. They are generally much larger than Ku-Band dishes, often ranging from 6 to 12 feet in diameter. The larger size allows them to maintain signal clarity, even in challenging conditions like heavy rainfall. This characteristic makes C-Band particularly beneficial for regions prone to weather-related signal interference, ensuring reliable communication where smaller dishes might fail.
_1742543367_WNo_1600d900.webp)
Primary Uses of C-Band Satellite Dishes
Television Receive-Only (TVRO) Systems
One of the most common uses of C-Band Satellite Dishes is in Television Receive-Only (TVRO) systems. TVRO systems allow users to receive free-to-air satellite television signals without the need for a cable subscription. This was particularly popular before the rise of digital cable and satellite TV. With C-Band dishes, users can access a wide variety of international and domestic channels—sometimes even in high-definition—without incurring additional costs.
Data and Communication Services
Apart from television, C-Band Satellite Dishes are widely used for data communication services. These dishes are ideal for providing internet access, telephony services, and secure data transmission, especially in remote or underserved areas. Industries like oil, maritime, and mining rely on C-Band for connecting operations in locations where traditional infrastructure is impractical or impossible. The durability and reach of C-Band signals make it a popular choice for satellite-based communication in these regions.
Advantages Over Other Satellite Bands
Resistance to Weather Interference
One of the standout advantages of C-Band is its resistance to weather-related interference. Signals transmitted at C-Band frequencies are less affected by rain fade and other weather phenomena compared to higher frequency bands, such as Ku-Band. This makes C-Band the preferred choice for regions that experience frequent storms, heavy rain, or snowfall. The larger wavelengths of C-Band signals allow them to travel longer distances and maintain stability, ensuring more reliable communication during adverse weather.
Larger Coverage Area
Another significant advantage is that C-Band offers a much larger coverage area with fewer satellites. The lower frequency range allows for wider signal distribution, meaning fewer satellites are required to provide broad geographic coverage. This is especially valuable in areas like Africa, the Middle East, and Asia-Pacific, where satellite services are essential but terrestrial infrastructure may be lacking or costly to build. The broader footprint of C-Band ensures a more efficient service delivery in these regions.
_1742543391_WNo_1600d900.webp)
Setting Up and Maintaining a C-Band Satellite Dish
Installation Process
Installing a C-Band Satellite Dish involves a precise and careful process to ensure optimal performance. The dish needs to be accurately aligned toward the satellite’s footprint, which requires adjusting the azimuth, elevation, and polarization angles. Proper alignment ensures that the satellite signal is strong and clear. Additionally, the dish should be installed in an open area with an unobstructed line of sight to the sky. Given the size of C-Band dishes, professional installation is often recommended to guarantee that everything is set up correctly.
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance is crucial to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of a C-Band Satellite Dish. Over time, dirt, dust, and other debris can accumulate on the dish, leading to degraded signal quality. Regular cleaning is necessary to maintain peak performance. Additionally, periodic inspections should be carried out to check for misalignment or any wear and tear on the Low Noise Block (LNB) converter, which is responsible for receiving satellite signals. Proper maintenance ensures that your C-Band satellite dish continues to provide reliable service.
Conclusion
While C-Band Satellite Dishes may no longer dominate residential satellite services, they remain an essential tool in professional satellite communication systems. Their ability to withstand harsh weather conditions, provide wide coverage, and ensure reliable data transmission makes them indispensable for ISPs, broadcasters, and satellite network operators. Whether for free-to-air television, broadcast contribution feeds, or remote communication services, C-Band continues to serve as a trusted solution in the satellite communications industry.
At NewStar, we specialize in providing comprehensive satellite communication solutions, including the research, development, production, system integration, installation, commissioning, training, and operational support of satellite communication antennas. Our expertise ensures that your satellite communication needs are met with the highest standards of quality and reliability. Explore our services today to enhance your communication infrastructure.